Pre-requisites-
- A MongoDB dump stored in Azure Blob Storage (e.g., from mongodump).
- A Cosmos DB for MongoDB vCore cluster with connection string and credentials.
- Azure Cloud Shell access.
- Install mongorestore in Cloud Shell (MongoDB tools).
Steps to perform backup and restore-
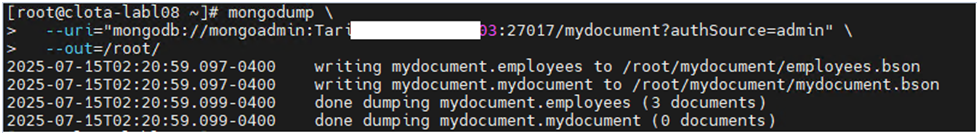
Step-1: Connect to the source MongoDB server and take a data dump using the mongodump utility.
mongodump \
–uri=”mongodb://mongoadmin:Password@Server_IP:27017/mydocument?authSource=admin” \
–out=/root/
Step-2: Install AzCopy on Linux by using a package manager.
Download the repository configuration package.
curl -sSL -O
https://packages.microsoft.com/config/<distribution>/<version>/packages-microsoft-prod.rpm
Install the repository configuration package.
sudo rpm -i packages-microsoft-prod.rpm
Delete the repository configuration package after you’ve installed it.
rm packages-microsoft-prod.rpm
Update the package index files.
Sudo dnf update
Install AzCopy.
Sudo dnf install azcopy
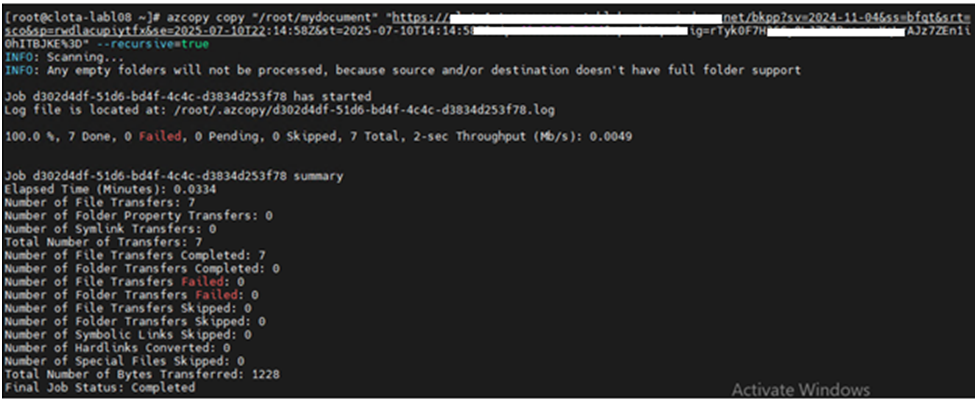
Step-3:Copy the MongoDB dump file from the source server to a Microsoft Azure Blob Storage container using the AzCopy tool.
azcopy copy “/root/mydocument” “https://storageaccountname.blob.core.windows.net/bkpp?sv=2024-11-04&ss=bfqt&srt=sco&SAS:14:58Z&st=2025-07-10T14:14:58Z&sip=49.207******************%2BvsrsuXqLrAJz7ZEn1i0hITBJKE%3D” –recursive=true
“/root/mydocument–Dump Location
https://containername.blob.core.windows.net/bkpp?—- Container Name
sv=2024-11-04&ss=bfqt&srt=**********************:14:58Z&st=2025-07-10T14:14:.207******************rAJz7ZEn1i0hITBJKE%3D”——Statistical Analysis System
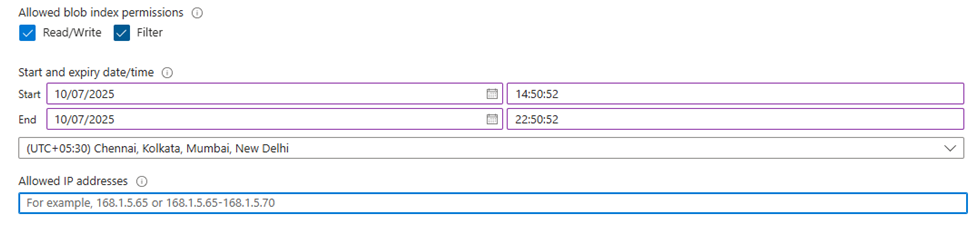
Generate SAS token:
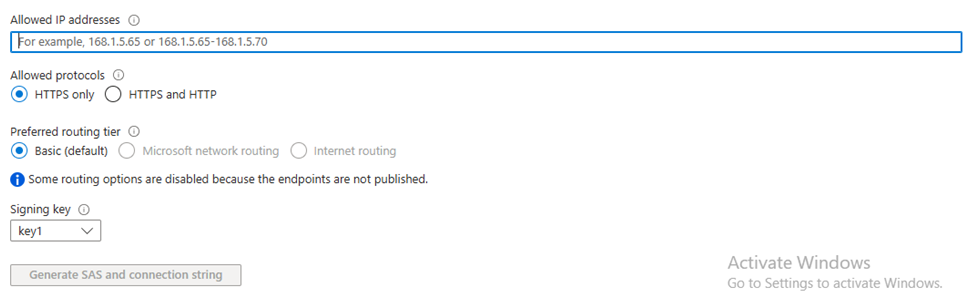
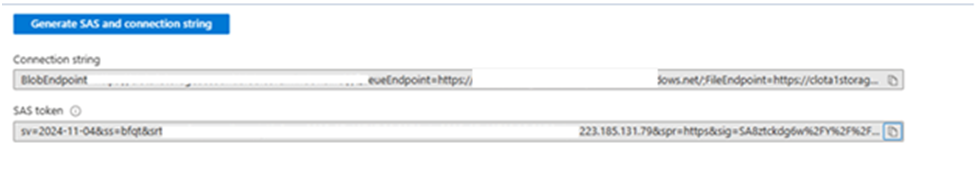
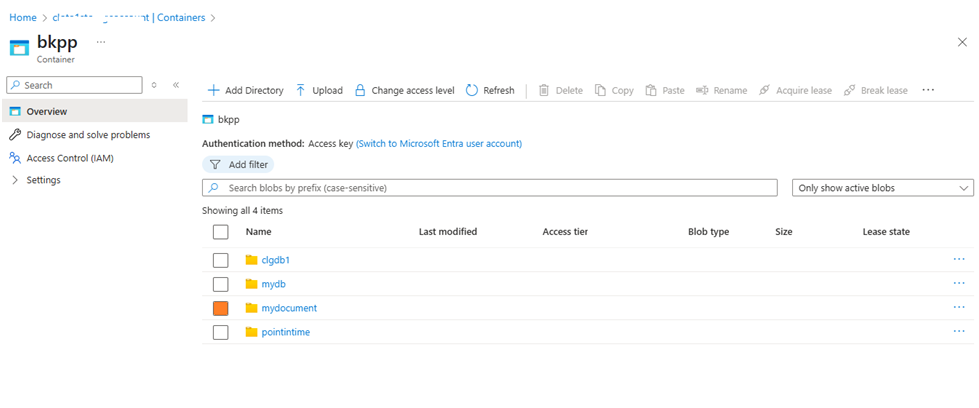
Step-4: Connect to the Microsoft Azure portal, navigate to the Blob Storage account, open the target container, and locate the uploaded backup (bkpp) folder.
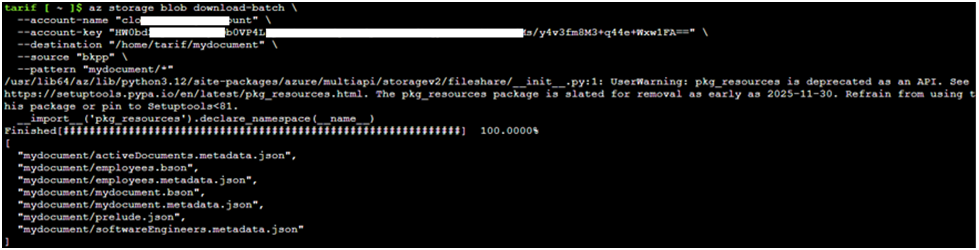
Step-5: Download the backup file from Azure Blob Storage to your local environment or Azure Cloud Shell using the AzCopy tool
az storage blob download-batch \
–account-name “account_name” \
–account-key “Account_key” \
–destination “/home/tarif/mydocument” \
–source “bkpp” \
–pattern “mydocument/*”
Step-6: Install MongoDB Tools in Azure Cloud Shell
- wget https://fastdl.mongodb.org/tools/db/mongodb-database-tools-ubuntu2004-x86_64-100.9.4.tgz
- tar -xvzf mongodb-database-tools-*.tgz
- echo ‘export PATH=$HOME/mongodb-tools/mongodb-database-tools-*/bin:$PATH’ >> ~/.bashrc
Step-7: Connect to Azure Cosmos DB and run the command to list all available databases to verify the connection and check existing databases.
Show dbs

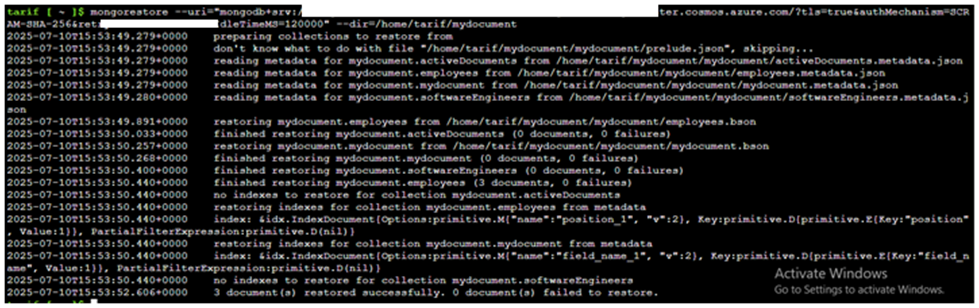
Step-8: Restore the MongoDB backup to Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB vCore directly from Azure Blob Storage using Azure Cloud Shell by downloading the backup with azcopy and restoring it using mongorestore.
mongorestore --uri "mongodb://myuser:[email protected]:10255/?ssl=true"
--dir”/home/tarif/mydocument"
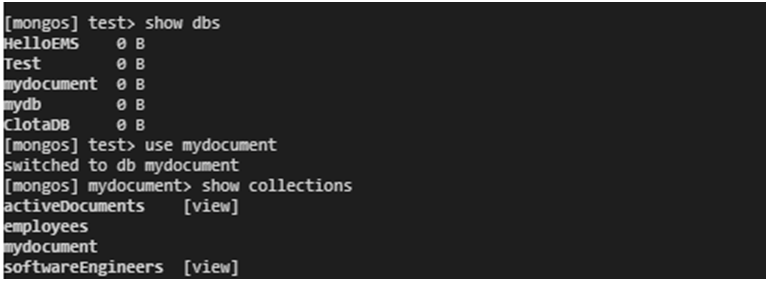
Step-9: Verify that the database and its collections have been successfully restored by connecting to Azure Cosmos DB and listing the databases and collections.
Show dbs
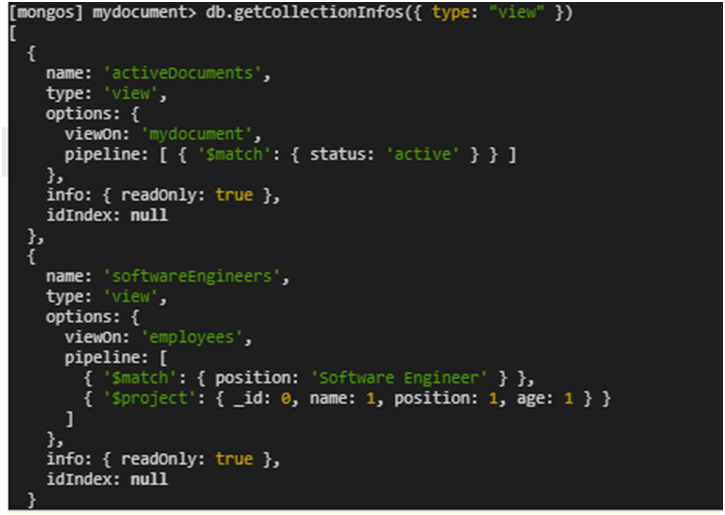
- To check if any views were restored, connect to the database and run a query to list all collections and filter those of type
view
db.getCollectionInfos({ type: "view"})
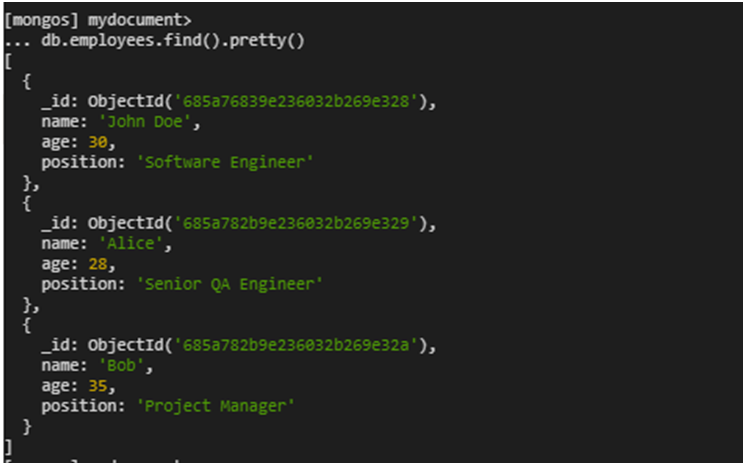
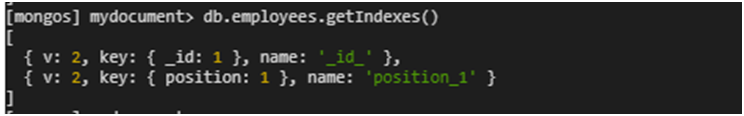
- Check that indexes have been successfully restored by listing all indexes for each collection in the database
db.employees.getIndexes()
Note: Indexes are migrated when you use:
mongodump –uri<source>
mongorestore –uri<target>
Limitations of Azure Cosmos DB for MongoDB vCore
- System Databases Not Migrated – Cannot migrate admin, local, or config databases.
- Users and Roles Not Transferred – MongoDB users, roles, and authentication settings are not migrated.
- Unsupported MongoDB Commands – Commands like isMaster, repairDatabase, etc., are not supported.
- No Server-side JavaScript or MapReduce – Features like db.eval() and mapReduce are not available.
- Partial BSON Type Support – Certain BSON types (e.g., DBRef) may not be fully supported.
- No Internal Auth User Migration – MongoDB internal authentication users cannot be migrated.
- Limited Aggregation Support – Aggregation stages like $lookup, $out, and $merge are not supported.
- Automatic Indexing -All fields are indexed by default, custom index control is limited.
- Limited Compound Indexes – Restrictions apply to compound indexes in certain scenarios.
- No Change Streams Support – Real-time change tracking via change streams is not available.
- TTL Index Limitations – Time-to-Live support is basic and limited.
- No Sharding After Deployment – Sharding is not supported once the cluster is created.
- Index Size Restriction – Index keys must be ≤ 2048 bytes.
- Max Document Size – Maximum document size is 2 MB.
- Supported MongoDB Versions – Only MongoDB 4.2 and 5.0 are supported. MongoDB 6.0+ is not yet supported.
- No Replica Set Customization – You cannot access or modify replicas set configurations.
- No Access to Server Logs or Configs – Direct access to MongoDB logs or config files is not provided.
- Limited Backup/Restore Features – Native backups are supported, but no point-in-time restore is available yet.
- Monitoring via Azure Monitor Only – Standard MongoDB logging tools like mongod.log are not accessible.
- No Instance-level Tuning – Cannot modify engine-level settings like WiredTiger options.

Leave a Reply